1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
|
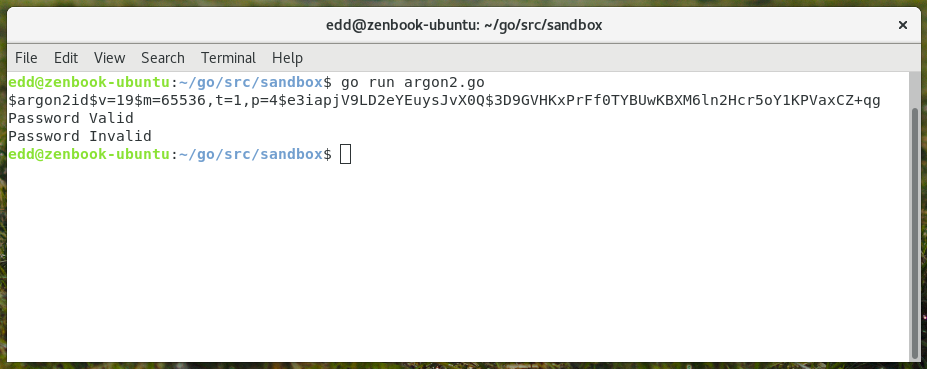
package main
import (
"crypto/rand"
"crypto/subtle"
"encoding/base64"
"fmt"
"strings"
"golang.org/x/crypto/argon2"
)
type PasswordConfig struct {
time uint32
memory uint32
threads uint8
keyLen uint32
}
func main() {
config := &PasswordConfig{
time: 1,
memory: 64 * 1024,
threads: 4,
keyLen: 32,
}
// Example 1: Generating a Password Hash
hash, err := GeneratePassword(config, "golangcode.com_pass")
if err != nil {
// handle error
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println(hash)
// Example 2: Check If Password if Valid (it is)
match, err := ComparePassword("golangcode.com_pass", hash)
if !match || err != nil {
fmt.Println("Password Invalid")
} else {
fmt.Println("Password Valid")
}
// Example 3: Test Incorrect Password
match, err = ComparePassword("I❤Liverpool", hash)
if !match || err != nil {
fmt.Println("Password Invalid")
} else {
fmt.Println("Password Valid")
}
}
// GeneratePassword is used to generate a new password hash for storing and
// comparing at a later date.
func GeneratePassword(c *PasswordConfig, password string) (string, error) {
// Generate a Salt
salt := make([]byte, 16)
if _, err := rand.Read(salt); err != nil {
return "", err
}
hash := argon2.IDKey([]byte(password), salt, c.time, c.memory, c.threads, c.keyLen)
// Base64 encode the salt and hashed password.
b64Salt := base64.RawStdEncoding.EncodeToString(salt)
b64Hash := base64.RawStdEncoding.EncodeToString(hash)
format := "$argon2id$v=%d$m=%d,t=%d,p=%d$%s$%s"
full := fmt.Sprintf(format, argon2.Version, c.memory, c.time, c.threads, b64Salt, b64Hash)
return full, nil
}
// ComparePassword is used to compare a user-inputted password to a hash to see
// if the password matches or not.
func ComparePassword(password, hash string) (bool, error) {
parts := strings.Split(hash, "$")
c := &PasswordConfig{}
_, err := fmt.Sscanf(parts[3], "m=%d,t=%d,p=%d", &c.memory, &c.time, &c.threads)
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
salt, err := base64.RawStdEncoding.DecodeString(parts[4])
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
decodedHash, err := base64.RawStdEncoding.DecodeString(parts[5])
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
c.keyLen = uint32(len(decodedHash))
comparisonHash := argon2.IDKey([]byte(password), salt, c.time, c.memory, c.threads, c.keyLen)
return (subtle.ConstantTimeCompare(decodedHash, comparisonHash) == 1), nil
}
|